<- main page <- Lecture 2 Lecture 3->
January 12, 2007
| 2.1 | Outline of Topics | ||
| Braitenberg Vehicles | |||
| I | |||
| II | |||
| III | |||
| Resources | |||
| Schools of Thought in AI | |||
| Classical AI / "good old-fashioned AI" (GOFAI) | |||
| Behavior-based robotics | |||
| Missing in Action | |||
| Example Agents | |||
| 2.2 | Braitenberg Vehicles I | |

|
||
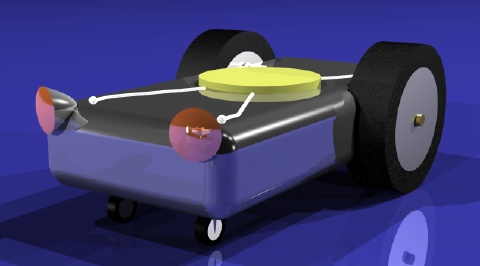
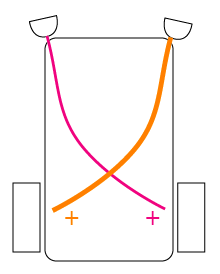
Braitenberg Vehicle |
||
Ingredients |
||
2 sensors |
||
2 motors |
||
2 Wires |
||
 |
 |
|
"Love" |
"Hate" |
|
| 2.3 | Braintenberg Vehicles II | |
 |
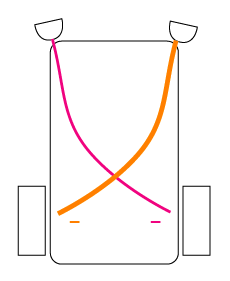 |
|
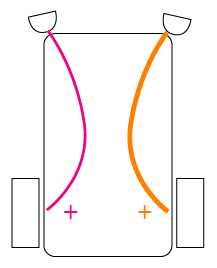
"Inverse love" |
"Inverse hate" |
|
| 2.4 | Braintenberg Vehicles III | |
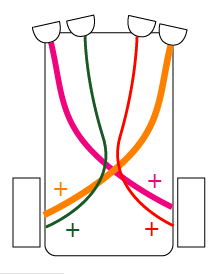 |
||
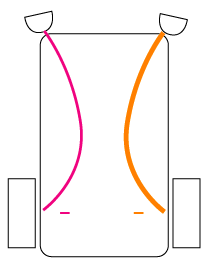
"Curious" |
||
| Outer light sensors | Strong positive cross-connections make vehicle steer towards light |
|
| Inner light sensors | Weak positive same-side connections make vehicle steer away from light | |
| Resulting behavior | Vehicle will move towards light that is far away but when it comes closer it will not crash into it | |
| 2.5 | Valentino Braitenberg Vehicles Resources | |
| Valentino Braitenberg: Vehicles - Experiments in Synthetic Psychology MIT Press |
||
Braitenberg Vehicles simulator - Downloadable
Java code |
http://www.mindspring.com/~gerken/vehicles/download/index.html | |
Braitenberg Vehicles simulator - applet |
http://www.architecture.yale.edu/872a/week4/braitenberg/ | |
MAVRICK - a robot architecture inspired by Braitenberg |
http://faculty.washington.edu/gmobus/AdaptiveAgents/MAVRIC-EBA.html | |
Java simulator |
http://www.ifi.unizh.ch/~pfeifer/mitbook/braitenberg/braitenberg.html | |
| 2.6 | Schools of thought in AI | |
| Cybernetics | Starting in the 1940s. Example works: Norbert Wiener's 1948 "Cybernetics, or Control and Communication in the Animal and Machine" and continued work such as WHAT THE FROG'S EYE TELLS THE FROG'S BRAIN by Lettvin, Maturana, McCullochs & Pitts, 1968. | |
| Emphasis |
|
|
| Classical AI / "good old-fashioned AI" (GOFAI) | Starting 1956: The Dartmouth Conference | |
| Emphasis |
|
|
| Behavior-based robotics | Starting around 1985 with R. Brooks' work on subsumption architecture | |
| Emphasis |
|
|
| Cognitive Science | An effort to integrate knowledge from psychology, neurophysiology, engineering, computer science, philosophy, lingustics in the study of mind. Initially pushed forward by Carnegie-Mellon. Possibly what the Cybernetics movement intended to become. | |
| 2.7 |
Classical AI | |
| "Classical AI": Top-down approach |
Term used to describe "reflective" or "deliberative" approaches to AI |
|
| Example typical topic (i.e. caricature) |
|
|
| Contrast with "Behavior-Based AI" | "Classical AI": Sometimes it means:
and somtimes it means:
|
|
| Classical AI: Topics |
"Top-down" approach |
|
| Classical AI: What it's good for |
|
|
| Missing pieces |
|
|
| 2.8 |
Behavior-Based AI | |
| "Behavior-based AI" |
Term used to describe "reactive" architectures with a tight coupling of sensors and actuators |
|
| Example typical topic (i.e. a caricature) |
Autonomous vaccum cleaner |
|
| Contrast with "Classical AI" | "Behavior-based AI": Sometimes it means:
and somtimes it means:
|
|
| Behavior-based AI: Topics |
"Bottom-up" approach |
|
| Behavior-based AI: What it's good for |
|
|
| Book
|
Ronald Arkin: Behavior-Based Robotics, MIT Press |
|
Java simulator |
http://www.ifi.unizh.ch/~pfeifer/mitbook/braitenberg/braitenberg.html | |
| 2.9 |
Missing in Action | |
| In classical AI |
|
|
| Behavior-based AI |
|
|
| In both classical and behavior-based AI |
|
|
| Hybrid approaches | Combine ideas from both classical and behavior-based AI, and often other schools of thought | |
| 2.10 |
Example Agents | |
| Cog |
|
|
| Attila / Genghis |
|
|
| Gandalf |
|
|
| Others |
|
|

RODNEY BROOKS WITH COG

ATTILA - SIX-LEGGED ROBOT AT MIT

GANDALF: COMMUNICATIVE VIRTUAL HUMANOID AT MIT